BioCELL mitoTOX
A highly specific and sensitive real-time cellular bioenergetic assay that combines rapid, straightforward assay designs with intuitive data interpretation for either compound-screening or dose‑response assays.
Distinguish between major modes of mitochondrial toxicity.
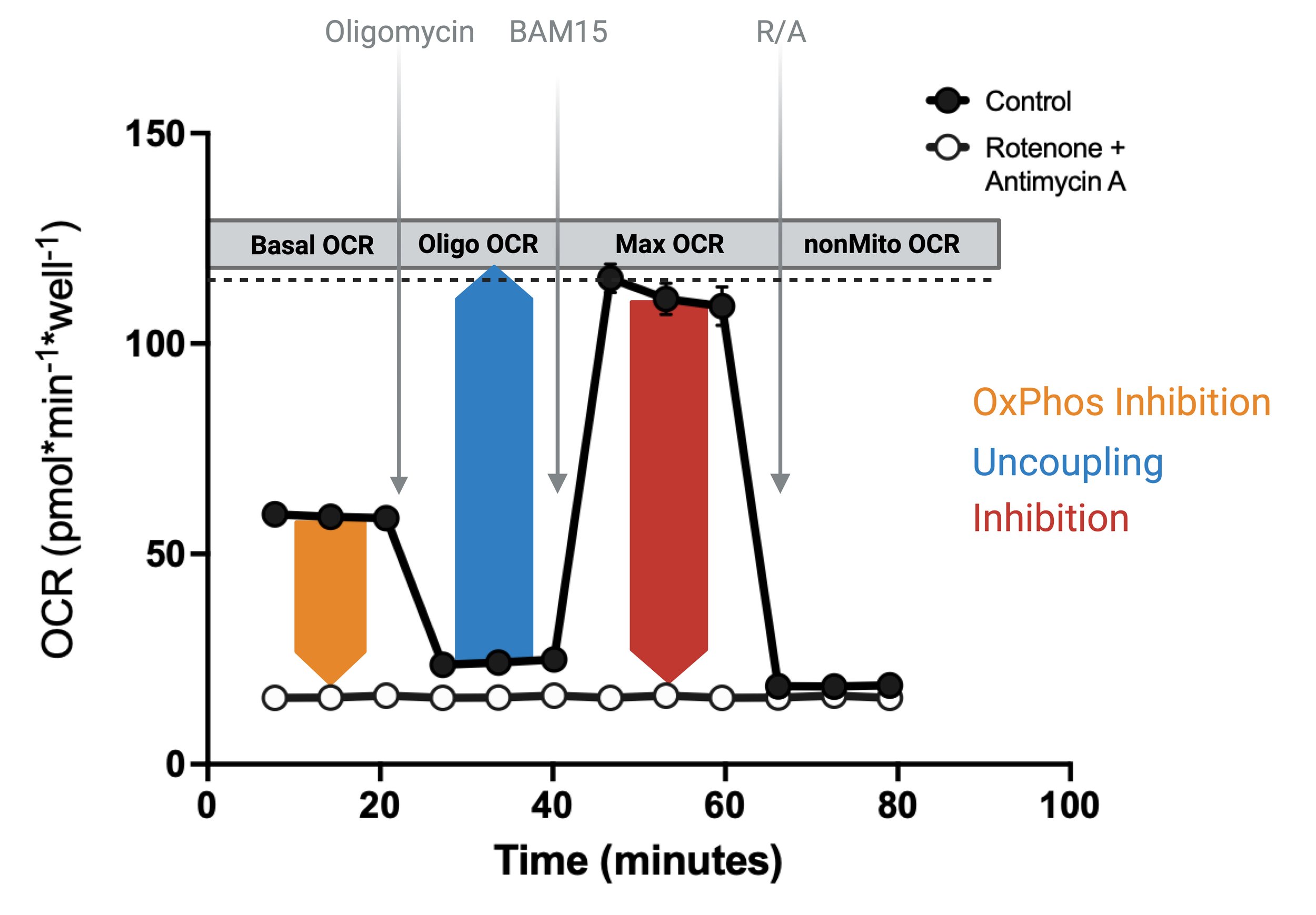
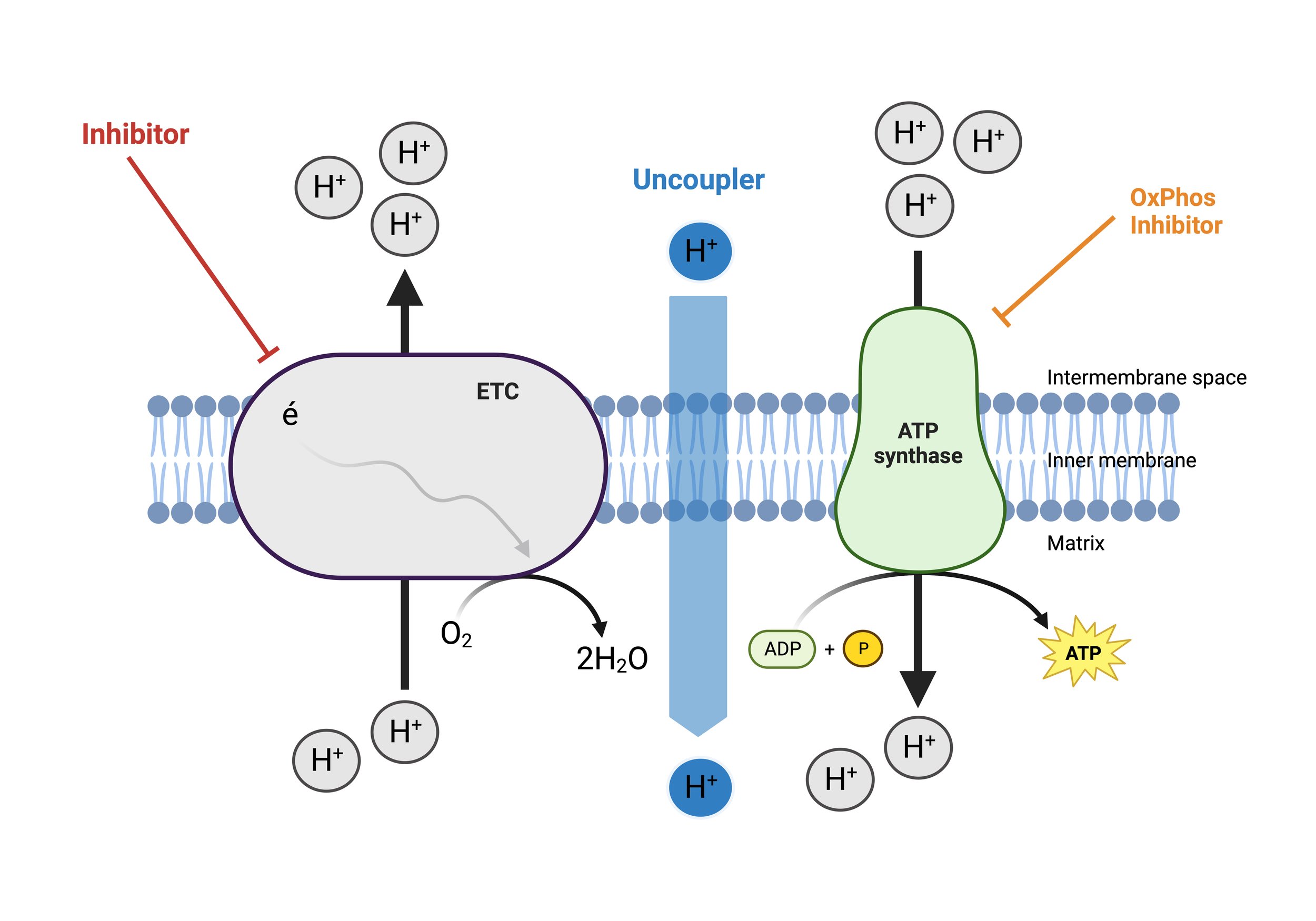
The figure shown here shows the different sites of mitochondrial toxicity identified by our BioCELL mitoTOX assay. (Top) Assay kinetic graph illustrating control groups (vehicle and Rot/AA) with injections. The effect of inhibitors, uncouplers, and OxPhos inhibitors (OPIs) are detected by measuring changes in maximal OCR, Oligo OCR, and Basal OCR, respectively. (Bottom) Compounds that exert effects on transport, TCA, FAO, ETC, or other upstream processes that result in decreased basal and maximal OCR are categorized as inhibitors. Compounds that act as protonophores that uncouple the ETC from the OxPhos machinery that result in increases in basal and oligo OCR are categorized as uncouplers. Compounds that specifically result in suppression of the OxPhos machinery (i.e., ATP synthase, adenine nucleotide transporter, inorganic phosphate transporter) are categorized as OPI and decrease basal OCR without significant effects on max OCR.
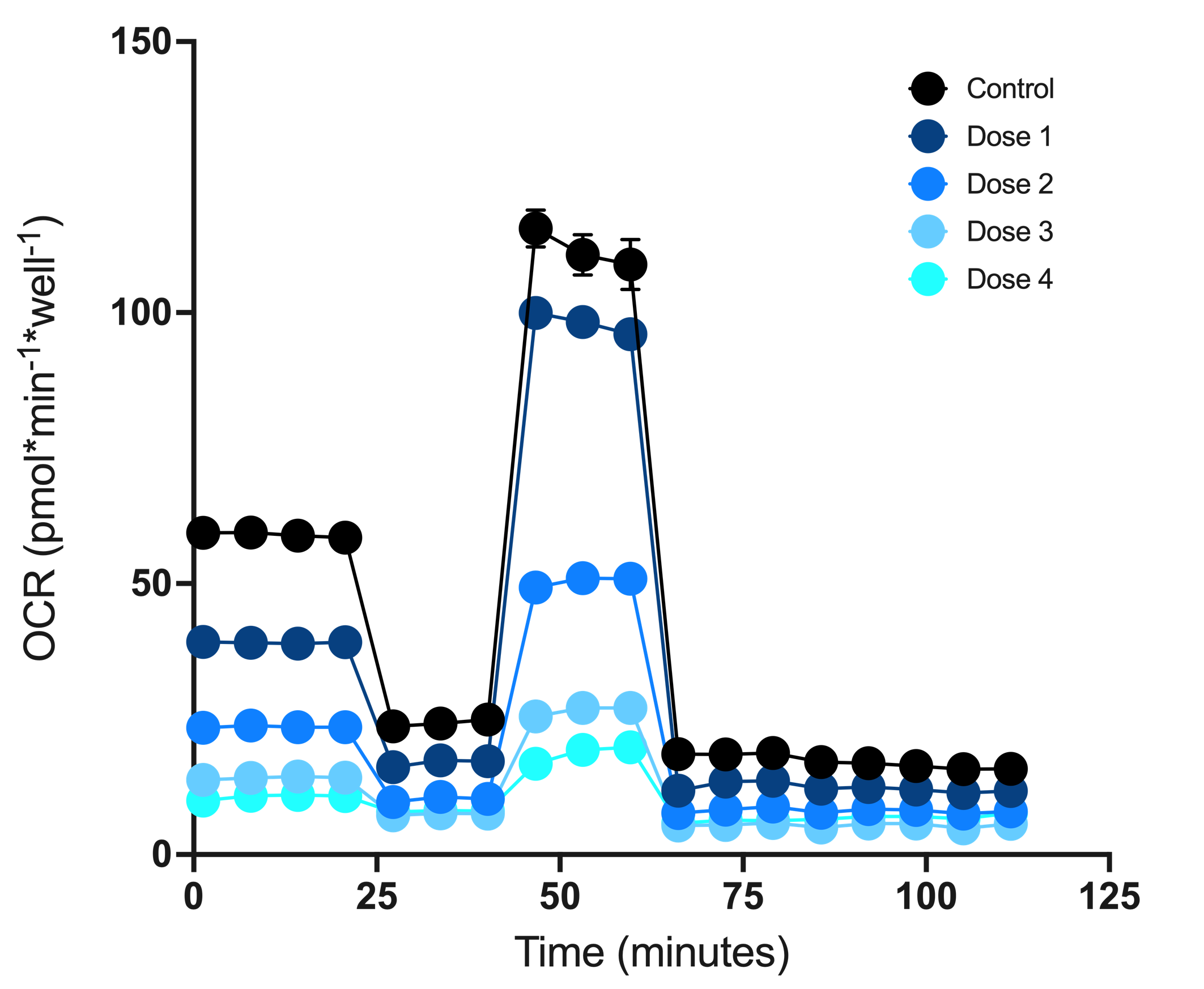
In the example data shown here, quantification using the MTI metric identifies compound X to be an inhibitor of mitochondrial function. An inhibitor leads to a decrease in OCRmax (and in some cases OCRbasal) but has limited effect on uncoupling.
The MTI also highlights a dose dependent effect of compound X on the level of toxicity. Inhibition can be mediated by effects on transport, TCA cycle, FAO, ETC, or other upstream process in which some component of mitochondrial function has been disrupted or inhibited. Uncoupled cells increase the specificity required to identify inhibitors, and increase the dynamic range for detection of inhibition compared to measurement of only Basal OCR.
Establish the magnitude of toxicity of compounds using the mitochondrial toxicity index (MTI).
Determine the potency of your drug on mitochondrial health.
Investigate the potency of mitochondrial toxic compounds using a dose-response assay. In the example shown, kinetic OCR measurements show changes in mitochondrial respiratory function in response to compound X (Top). By expressing MTI as a function of compound dose, the potency of mitochondrial inhibition can be determined with respective IC50 values.
For compounds that present as mitochondrial uncouplers, potency is determined by expressing MTI values as a function of compound dose with respective EC50 values.
Key Features.
-

Real-time kinetic measurements
-

Live cell samples
-

Multi-parameter analysis
-

High sensitivity
-

High-throughput screening
FAQs
-
This assay works for any cell line or primary cell type that has functional mitochondria. We can offer access to a range of different cell types including HEK293, HepG2, INS-1E, MCF-7, C2C12, PBMCs, T-lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages.
-
Upto 40 compounds at a single dose.
-
In some cases we would recommend optimising the assay, for example if a specific cell type or cell model is being used. We will also support any optimisation using our BioCELL optiMIZE assay service.
-
Yes. We run a post-hoc fluorescent based nuclear stain cell density test. This is key to normalise any cytotoxic effects of compounds that might skew the results. Whereby this test is not suitable for the cell model being used we can also offer total protein or dsDNA for normalisation.
Interested in using our service?
Fill out the form below to arrange a free consultation with on of our experts.